2016 年 11 月 29 日 17:02:35 / no comments
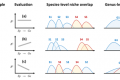
Hsiao-Pei Lu and Chih-hao Hsieh Institute of Oceanography, National Taiwan University Species is considered as the fundamental unit for ecological studies. Nevertheless, it is notable that living organisms are hierarchically organized: individuals can be classified into species, species into genera, genera into families, and so on. Previous studies on [...]
2016 年 11 月 08 日 14:26:12 / no comments
2016 年 10 月 12 日 09:17:12 / no comments
Speaker:Dr. Akifumi S. Tanabe (National Research Institute of Fisheries Science, Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency) Title:Bridging between NGS data and community ecology: Methods and an application. Time:10/12 (Wed) 13:30 Location:2nd floor large lecture hall of IONTU Abstract DNA barcoding technique enabled us to reuse identification results by experts using [...]
2013 年 12 月 19 日 13:42:17 / no comments
In order to quantitatively predict the impact of loss of species number on the provision of ecosystem services therefore human well-being, it is necessary to evaluate the functional redundancy of ecosystem. However, the functional redundancy has been overestimated due to the insufficient appreciation on complexity and multidimentionality of ecosystem functioning. [...]
2013 年 07 月 15 日 14:53:18 / no comments
Lin Ye and Chih-hao Hsieh Institute of Oceanography, National Taiwan University With the aid of new technologies to measure zooplankton size and community structure, a group of scientists of National Taiwan University formulated a novel hypothesis: increasing predator size diversity enhances the strength of top-down control on prey [...]
2013 年 05 月 03 日 15:20:03 / no comments
Associate Professor, Chih-hao Hsieh, from the Institute of Oceanography/Institute of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, together with an international research team develops a method that helps examine nonlinear climate impacts on Pacific sardines. This study, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (4/17/2013), provides a new solution to forecast [...]
2012 年 10 月 29 日 16:46:21 / no comments
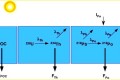
Seasonal Changes in Gaseous Elemental Mercury in Relation to Monsoon Cycling over the Northern South China Sea Tseng, C. M., Liu, C. S., Lamborg, C., (2012), Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 7341-7350, doi:10.5194/acp-12-7341-2012. www.atmos-chem-phys.net/12/7341/2012/ The distribution of gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) was determined in the surface atmosphere of the northern South [...]
2012 年 10 月 25 日 14:25:16 / no comments
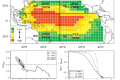
Stock assessments that include a spatial component or relate population dynamics to environmental conditions can be considered one way of implementing an ecosystem approach to fisheries. A spatially-structured population dynamics model that takes account of habitat preference is developed and then applied to Pacific blue marlin (Makaira nigricans), as they [...]
2012 年 10 月 25 日 14:17:53 / no comments
Crustaceans play an important role in marine ecosystem and worldwide fisheries. Accurate and quantitative description of growth is crucial in modelling the demographics and fisheries stock assessment. The stepwise growth as a result of the moulting process and the lack of permanent calcified structures make the traditional approaches developed for [...]
2012 年 10 月 24 日 14:51:25 / no comments
The Coral Triangle is known as marine biodiversity center according to its highestmarine biodiversity.However, the mechanism to form such a high biodiversity is still under debate. Pomacentruscoelestisis also known as neon damselfish which distributed across coral triangle has been used as a model species to reveal its phylogeographic structure and [...]
2012 年 10 月 22 日 16:33:38 / no comments
The research work in my (Wei-Jen Chen’s) lab can be summarized as the application of molecular and computational tools within a phylogenetic framework to interpret organismal diversity and to understand mechanisms of evolution (see: http://wjchen.actinops.googlepages.com/). The research accomplishments in 2012 have been focused on molecular systematics of two cypriniform fish [...]
2012 年 10 月 22 日 16:04:25 / no comments
Research topic 1 – Migratory life history of deep sea fishes We analyzed otolith microstructures and stable isotope of deep sea fishes to reveal their ontogenetic vertical (downward) migration. Otolith microstructures and δ18O showed different migratory patterns, e.g., migration timing and distances, among species. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967063711002378 Research topic 2 –Eutrophication reduce [...]
2012 年 07 月 12 日 15:19:13 / no comments
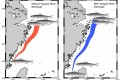
“Damned” Yangtze River Dam may affect the spawning migration of anchovy in the East China Sea Chen-Yi Tu and Chih-hao Hsieh Institute of Oceanography, National Taiwan University Using a coupled fish behavior–hydrodynamic model, a group of scientists of National Taiwan University suggest that the dammed Yangtze River could have negative [...]
2012 年 01 月 03 日 09:54:56 / no comments
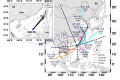
Title: Interacting ocean waves explain powerful sea floor canyon flows Off the southwestern coast of Taiwan the Gaoping Submarine Canyon meanders in a giant backwards “S” as it stretches southwestward toward the South China Sea. In the canyon, a 200-m-deep cut into the seafloor that lies 300 m below the [...]
2011 年 12 月 26 日 09:55:58 / no comments
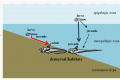
Particle-reactive radionuclides are very powerful tools in studying the cycling processes of chemical elements in the ocean. Among the naturally occurring radionuclides, 234Th, 210Pb, and 210Po have been used to investigate the carbon export via particle settling through the upper water column of the South China Sea and the particle removal fluxes [...]