Research highlights of Prof. Jen Chieh Shiao
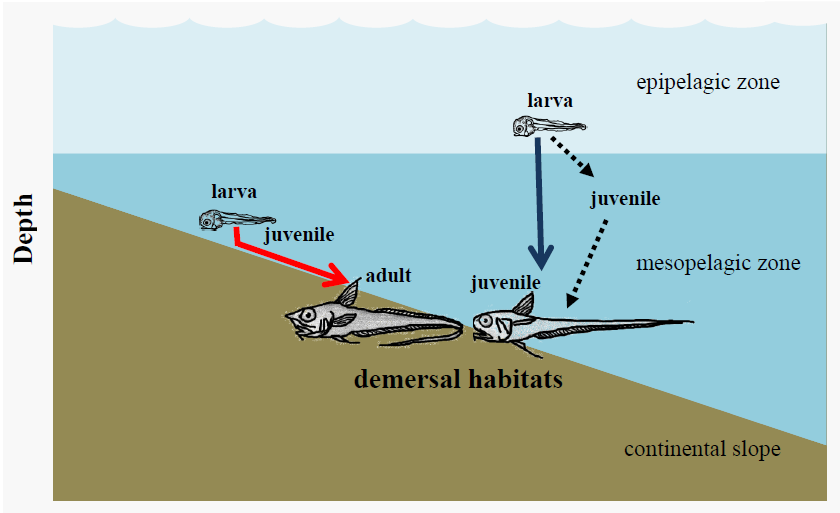
Research topic 1 – Migratory life history of deep sea fishes
We analyzed otolith microstructures and stable isotope of deep sea fishes to reveal their ontogenetic vertical (downward) migration. Otolith microstructures and δ18O showed different migratory patterns, e.g., migration timing and distances, among species.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967063711002378
Research topic 2 –Eutrophication reduce diversity of demersal fish in East China Sea.
Through oceanographic surveys for several years, we find that the inshore area of the East China Sea, corresponding to the prohibited zone for trawling, had extremely high nutrient concentrations and low dissolved oxygen. The diversity index of demersal fish showed significantly negative correlations with nutrient concentrations and positive correlations with bottom-water dissolved oxygen. The inshore area of the East China Sea was heavily dominated by small-sized fishes, reflecting low survival of most fish species. These findings suggest that eutrophication and subsequent hypoxia could have limited fish population growth in the trawling prohibition area of the East China Sea despite of absence of fishery operations. Therefore, a multi-pronged fishery management plan that involves both fishing restriction and environmental improvement is urgently needed in the East China Sea.
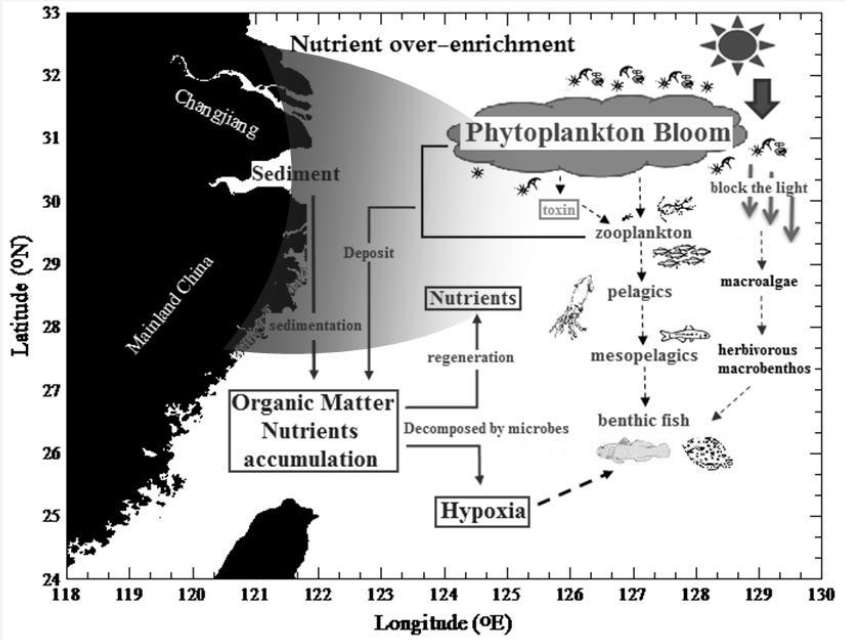
(圖二) 富營養化與底棲魚群關係的概念圖。虛線表示直接與間接的負影響,包括有毒的二級代謝物、有遮蔽的環境以及低溶氧的環境(< 3 mg l-1),灰色梯度表示著長江水從沿岸交換到遠洋的影響範圍。在三峽大壩的完工後,長江水交換影響的區域縮小。
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278434312001677
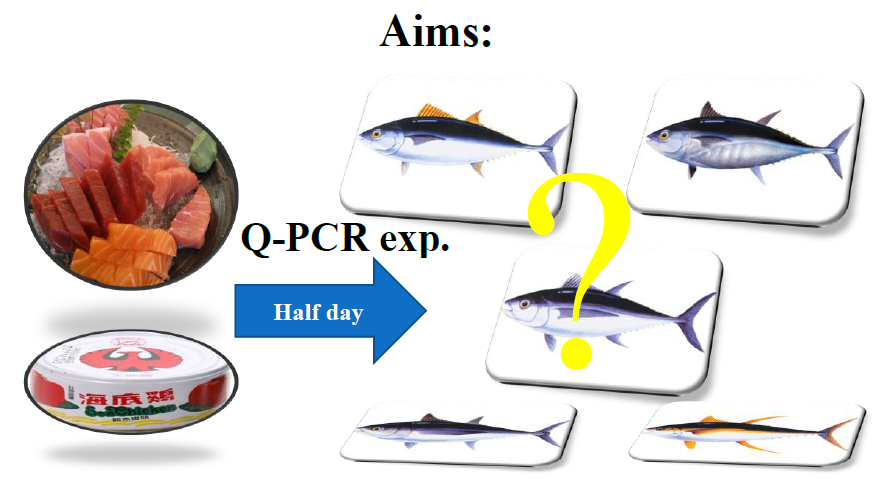
Research topic 3 – Rapid identification of tuna species by real-time PCR technique.
We develop species-specific probes and primers for rapid and high-throughput identification of tuna species. The probe and primer are designed to amplify the mitochondrial genes. This assay can be applied to fresh, alcohol preserved and canned samples. The whole procedure can be conducted within half-a-working day.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814612001288