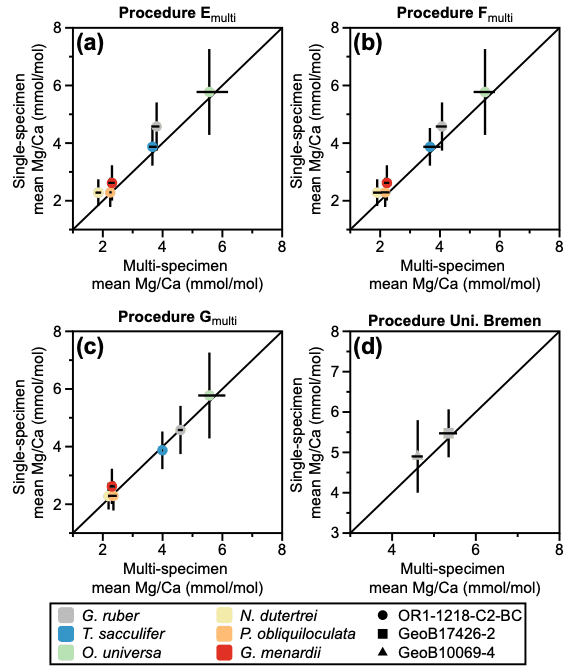
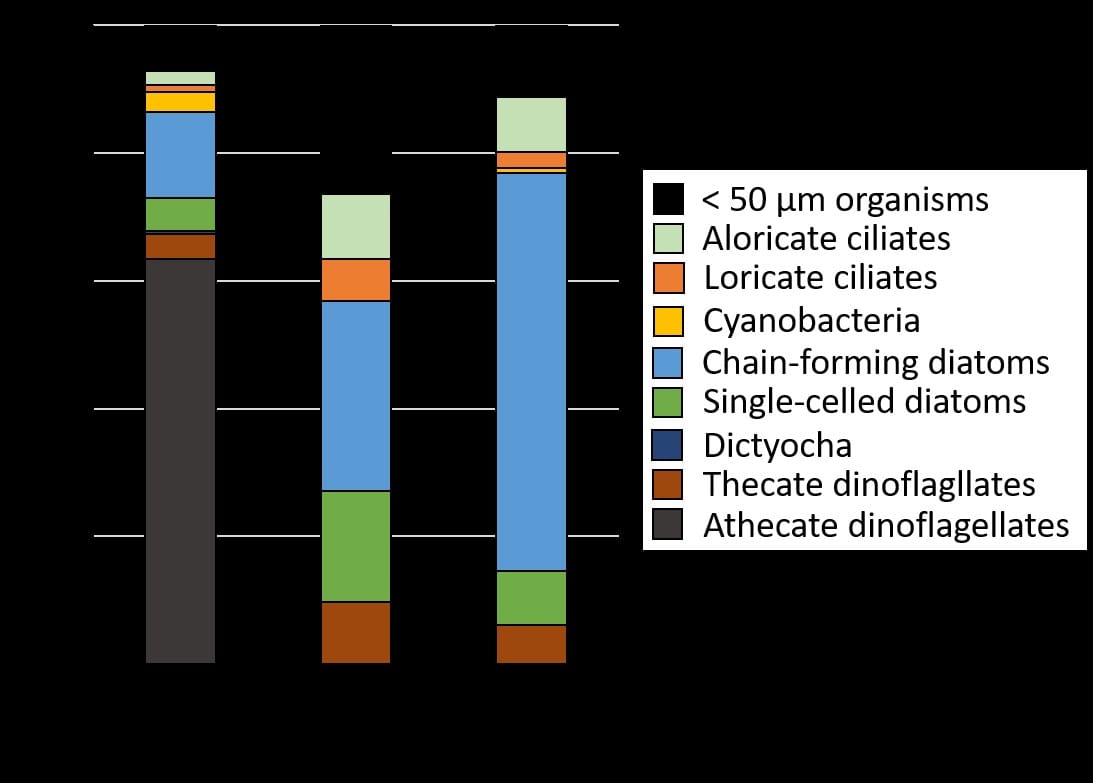
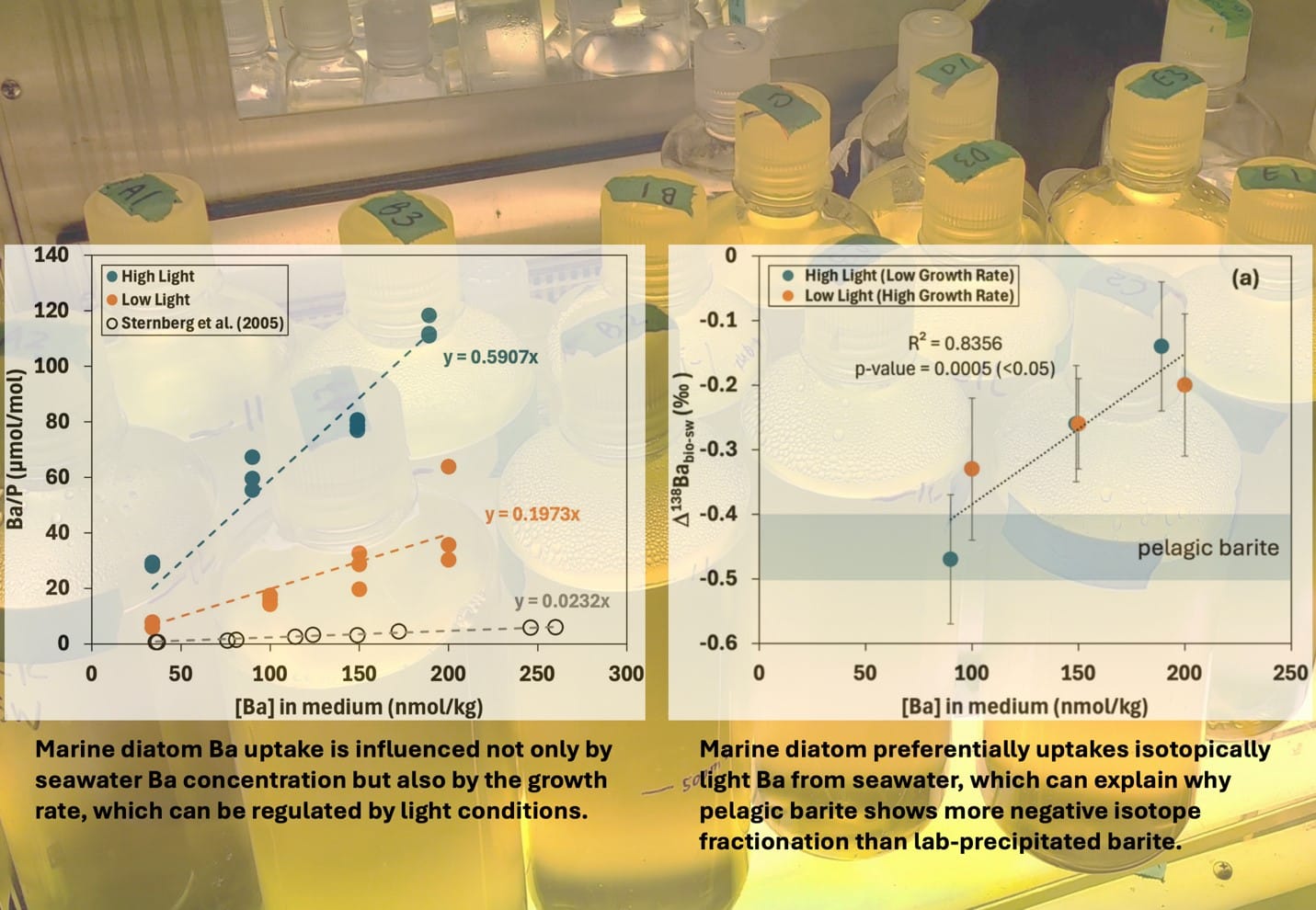
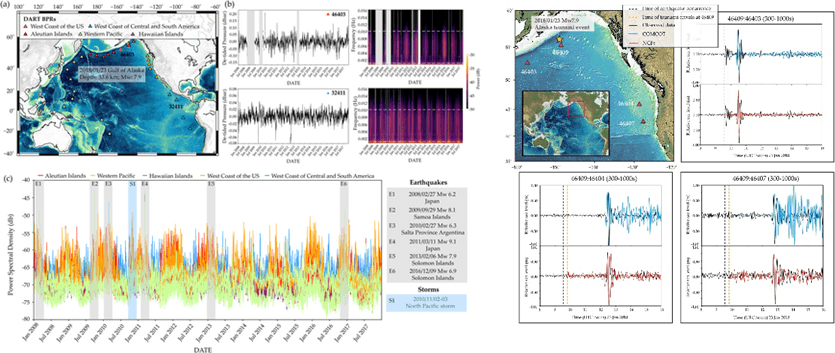
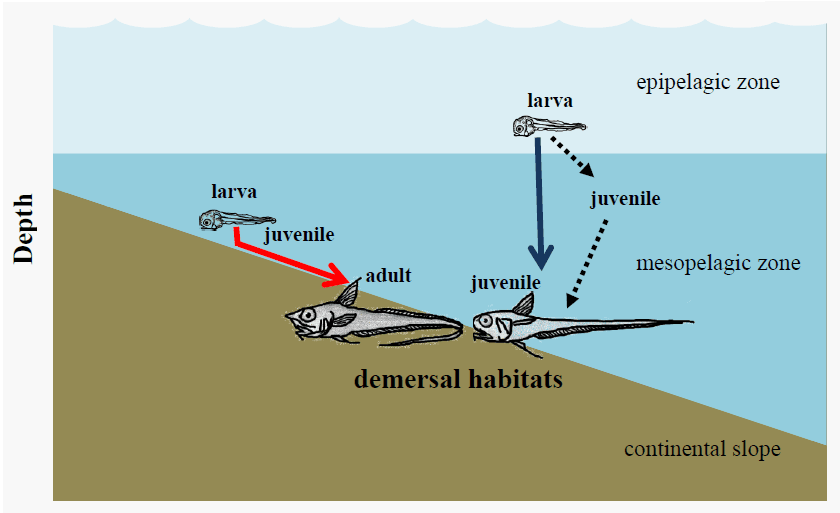
研究主題一:深海魚類的洄游生活史
我們對於深海魚類耳石的微結構和穩定性同位素進行分析,以了解深海魚類個體發育時的垂直遷移模式。分析結果顯示,不同魚種有不同的垂直遷移方式(例如遷移時間與距離的變異)。Jen Chieh Shiao
Research topic 1 – Migratory life history of deep sea fishes
We analyzed otolith microstructures and stable isotope of deep sea fishes to reveal their ontogenetic vertical (downward) migration. Otolith microstructures and δ18O showed different migratory patterns, e.g., migration timing and distances, among species.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967063711002378
Research topic 2 –Eutrophication reduce diversity of demersal fish in East China Sea.
Through oceanographic surveys for several years, we find that the inshore area of the East China Sea, corresponding to the prohibited zone for trawling, had extremely high nutrient concentrations and low dissolved oxygen. The diversity index of demersal fish showed significantly negative correlations with nutrient concentrations and positive correlations with bottom-water dissolved oxygen. The inshore area of the East China Sea was heavily dominated by small-sized fishes, reflecting low survival of most fish species. These findings suggest that eutrophication and subsequent hypoxia could have limited fish population growth in the trawling prohibition area of the East China Sea despite of absence of fishery operations. Therefore, a multi-pronged fishery management plan that involves both fishing restriction and environmental improvement is urgently needed in the East China Sea.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278434312001677
Research topic 3 – Rapid identification of tuna species by real-time PCR technique.
We develop species-specific probes and primers for rapid and high-throughput identification of tuna species. The probe and primer are designed to amplify the mitochondrial genes. This assay can be applied to fresh, alcohol preserved and canned samples. The whole procedure can be conducted within half-a-working day.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814612001288

http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967063711002378
研究主題二:東海優養化降低底棲魚類的多樣性
透過幾年來在東海海域的調查,我們發現在實施禁止拖網的近岸處有極高的營養鹽濃度以及極低的溶氧濃度。底棲魚群的多樣性指標與營養鹽濃度呈負相關趨勢,與底層水的溶氧濃度則呈現正相關趨勢。在東海近岸海域捕獲的大多數魚體長偏小,在此顯示出個體存活率低。這些發現說明優養化造成之低氧環境限制東海近岸海域的漁業資源恢復力,因此在東海海域多重的漁業管理策略,包括捕撈的限制以及環境的改善都是必要考慮的地方。
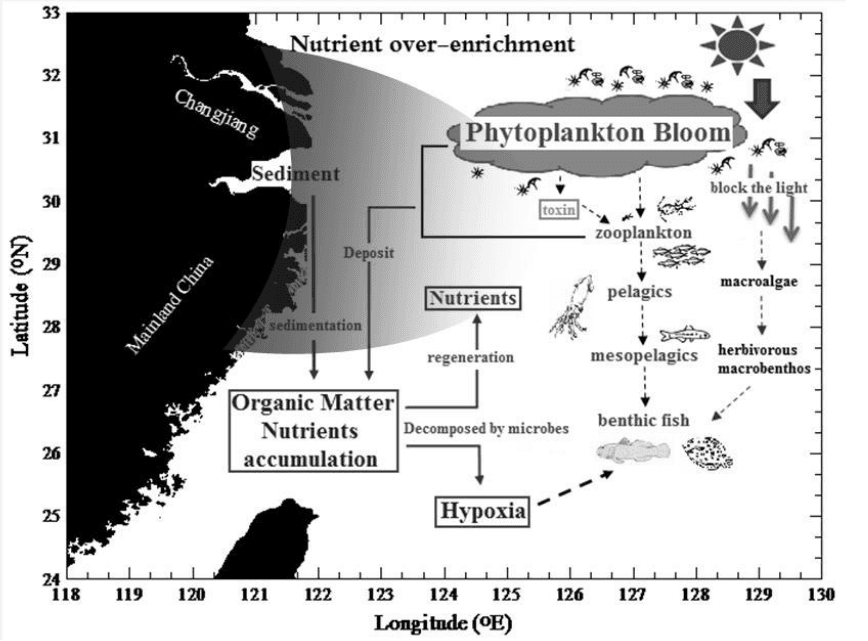
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278434312001677
研究主題三:以QPCR技術快速鑑定鮪魚種類
我們發展出一種以分子技術用於快速鑑定鮪魚種類。這種技術包括對於鮪魚魚種有專一性的探針以及引子,並以此來放大粒線體的基因片段。此方法可用於煮熟的鮪魚罐頭,新鮮樣本,或是經酒精保存過的樣本上,整個鑑定過程可於半天內完成。
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814612001288